Update:
2006-08-10 03:09 AM -0700
TIL
Medicinal Plants of Myanmar
Zingiberaceae
compiled by U Kyaw Tun, U Pe Than, and staff of TIL. Not for sale.
Contents of this page
Family: Zingiberaceae 8 entries
Zingiberaceae family - general characters ('Monocotyledoneae)
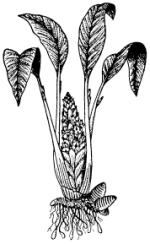
Alpinia galanga
{pa.tθ-kau:kri:}
Alpinia officinarum
{pa.tθ:kau:lι:}
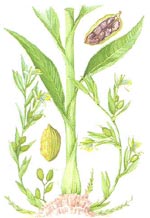
Curcuma longa
{na.nwing:}
 / {hsa.nwing:}
/ {hsa.nwing:}
Elettaria cardamomum
{hpa-la}
 /
{hpa-la-hpru}
/
{hpa-la-hpru}
Hedychium spicatum
{ngwι-pan:ping}
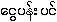
Kaempferia galanga {kwam:sa:ga.moan:}
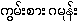
Zingiber cassumunar {maith~tha.ling}
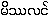
Zingiber officinale {hkying:
(gying:)} 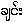 (
( )
)
Alpinea spp.
Hedychium spp.
Kaempferia spp.
Zingiber spp.
Main Index of DB | Top
Contents of this page
Zingiberaceae family - general characters ('Monocotyledoneae)
From: Families yielding important phytopharmaceuticals in
Fundamentals of Pharmacognosy and Phytotherapy, by Michael Heinrich, J.
Barnes, S. Gibbons, and E. Williamson, October 2003, ISBN:0443071322, pp.320 --
www.fleshandbones.com/readingroom/pdf/747.pdf
In terms of pharmaceutical usage, this family is the most important of the
former class Monocotyledoneae (which includes the Liliaceae, Palmaceae and
Poaceae). Many members of this family are native to the Indo-Malayan region and
are thus particularly important in Asian medical systems.
Important medicinal plants from the family
Curcuma zanthorrhiza Roxburgh (Temu lawak, Javanese turmeric).
Curcuma longa L. (syn. C. domestica, turmeric), a commonly used
spice and popular remedy used, for example, for inflammatory and liver diseases,
and in most Asian medical systems for a large variety of illnesses.
Elettaria cardamomum (L.) Maton (cardamom), which is mostly used as a
spice but also as a medicine.
Zingiber officinale Roscoe (ginger), used for a large variety of
illnesses, including travel sickness, respiratory and gastrointestinal
disorders.
Morphological characteristics of the family
Generally, the species of this family are aromatic herbs with very prominent
thickened rhizomes. The latter are often rich in essential oil, stored in
typical secretory cells.
The leaves are arranged spirally or are distichous with a sheath
around the stem (similar to the grasses). However, these sheaths are arranged in
such a way that they form a stem-like structure, which supports the real, rather
weak, stem. The zygomorphic and bisexual flowers are often very large and
prominent and are pollinated by large, often nocturnal, insects, birds or bats.
Distribution
The family is distributed throughout the tropics, but many species are
native to Asia (Indo-Malayan region).
Chemical characteristics of the family
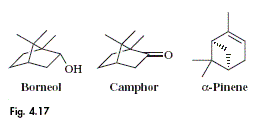
This family is one of the few families of the former Monocotyledons which is
rich in essential oil with terpenes such as borneol, camphor and cineole (all
oxygen-containing monoterpenes), camphene, pinene (monoterpenes) and zingiberene
(a sesquiterpene), as well as phenylpropanoids (cinnamic acid derivatives) (Fig.
4.17). Typically, these compounds accumulate in oil cells, an important
microscopical characteristic of the rhizomes of the Zingiberaceae.
Contents of this page
syn. A. conchigera
Family: Zingiberaceae
Burmese-Myanmar transcript names:
Agri.Dept.2000 34-0896:
 {pa.tθ:kau: kri:}
{pa.tθ:kau: kri:}
Chklist:
LSR 257 :
 {pa.tθ:kau: kri:}
{pa.tθ:kau: kri:}
FAO : NL
KS-TMN 222 : Pade-gaw-gyi
Nagathein 2-183:
 {pa.tθ:kau: kri:}
{pa.tθ:kau: kri:}
UHM : NL
Myanmar-Script Spelling :
Official Myanmar Dictionaries
 {pa.tθ:kau:} -
{pa.tθ:kau:} -
 --
TravPo-M-Dict 179
--
TravPo-M-Dict 179
 {pa.tθ:kau:} - n. an aromatic herb of the ginger family, Hedychium gracile --
Myan-Engl-Dict 250
{pa.tθ:kau:} - n. an aromatic herb of the ginger family, Hedychium gracile --
Myan-Engl-Dict 250
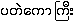 {pa.tθ:kau kri:} - n. greater galingale, Alpinia conchigera --
Myan-Engl-Dict 250
{pa.tθ:kau kri:} - n. greater galingale, Alpinia conchigera --
Myan-Engl-Dict 250
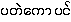 {pa.tθ:kau: ping} - Myan-Ortho - 140
{pa.tθ:kau: ping} - Myan-Ortho - 140
Chklist data:

 Hindi:
Hindi:
Sanskrit:
English common name used in Myanmar:
Agri.Dept.2000 34-0896: Greater galangal
Chklist:
LSR 257 : Greater galangal
FAO : NL
KS-TMN 222 : Greater Galangal
Nagathein 2-183: NG
UHM : NL
Picture
Leader
Photos: left -- close up of flowers, right -- close up of fruits.
Click on the pictures to enlarge. -- KS-TMN
Plant identification characters
A perennial herb; rhizomes horizontal, tuberous, thick,
fleshy, aromatic; aerial stems elongate, leafy; roots adventitious, arise from
rhizomes. Leaves cauline, alternate, distichous; petioles short; ligules
triangular; blades lanceolate to elliptical, the bases usually cuneate,
sometimes obtuse, the margins entire, undulate, the tips acute to acuminate,
venation closely parallel-pinnate, the upper surfaces glabrous, the lower
pubescent. Inflorescences terminal paniculate cymes; bracts small, ovate,
scarious. Flowers pedicellate, bisexual, zygomorphic, trimerous,
epigynous. Calyx synsepalous, 3-lobed, the lobes minute, triangular, the tubes
tubular, short. Corolla synpetalous, 3-lobed, the tubes cylindrical, the lobes
equal, elliptic-oblong, cucullate, the upper lobe broaderthan the laterals,
greenish white. Androecium polyandrous, the fertile stamen 1, stout arcuate, the
filament flattened, epipetalous at mouth of corolla tube, yellow above, reddish
below, the anthers dithecous, the lobes ellipsoid, divergent apically, yellow
the spur and crest absent, the lateral staminodes absent, the lip or labellum
orbicular, retuse, the margins incurved, cream coloured, with red streaks on
either side, the 2 basal auricles small, tooth-like, basifixed, introrse,
dehiscence longitudinal. Pistil 1, ovary globose, 3-lobed, 3-carpelled,
syncarpous, 3-loculed, the ovules numerous, the placentation axile with one row
of ovules in each locule, the style filiform, inserted within the grooved
filament of the fertile stamen, the stigma infundibuliform. Fruit a
loculicidal capsule, globose; seeds numerous, small, angled, arillate, aromatic,
endospermc. Flowering period: October-December, Fruiting period:
January-March -- KS-TMN
Distribution in Myanmar
Grows wild or cultivated throughout Myanmar. -- KS-TMN
Part used and uses
Rhizomes -- Expectorant; Cough; Sore throat; Carminative;
Indigestion; Purexia; Heart disease Oral infection; Dysuria. -- KS-TMN
Constituents
Contents of this page
Family: Zingiberaceae
Burmese-Myanmar transcript names:
Agri.Dept.2000 34-0895:
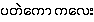 {pa.tθ:kau: ka.lι:}
{pa.tθ:kau: ka.lι:}
Chklist:
LSR 261 :
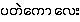 {pa.tθ:kau: lι:}
{pa.tθ:kau: lι:}
FAO : NL
KS-TMN : NL
Nagathein 2-185:
 {pa.tθ:kau: (ngθύ)}
{pa.tθ:kau: (ngθύ)}
UHM 04: Padegaw-gale
UKT: Three species of galangal (genus Alpinia, family Zingiberaceae) were
listed by Agri.Dept.2000 p. 34
34-0895: A. officinarum -- {pa.tθ:kau: ka.lι:} -- Lesser galangal
34-0896: A. galanga -- {pa.tθ:kau: kri:} -- Greater galangal
34-0897: A. nutans -- {pa.tθ:kau: lat} -- Nutral galangal
Myanmar-Script Spelling :
Official Myanmar Dictionaries
 {pa.tθ:kau:} -
{pa.tθ:kau:} -
 --
TravPo-M-Dict 179
--
TravPo-M-Dict 179
 {pa.tθ:kau:} - n. an aromatic herb of the ginger family, Hedychium gracile --
Myan-Engl-Dict 250
{pa.tθ:kau:} - n. an aromatic herb of the ginger family, Hedychium gracile --
Myan-Engl-Dict 250
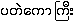 {pa.tθ:kau kri:} - n. greater galingale, Alpinia conchigera -- Myan-Engl-Dict 250
{pa.tθ:kau kri:} - n. greater galingale, Alpinia conchigera -- Myan-Engl-Dict 250
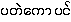 {pa.tθ:kau: ping} - Myan-Ortho - 140
{pa.tθ:kau: ping} - Myan-Ortho - 140
Chklist data:
Hindi:

Sanskrit:
English common name used in Myanmar:
Agri.Dept.2000 34-0895: Lesser galangal
Chklist:
LSR 261 : Lesser galangal
FAO : NL
KS-TMN : NL
Nagathein 2-185: NG
UHM 04: Lesser Galangal, Chinese Ginger, China Root, East Indian Root,
Rhizome Galangae -- UHM
Picture:
Leader -
www.botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/g/galang01.html
Inflorescence --
King's American Dispensatory. Harvey Wickes Felter, M.D.,
and John Uri Lloyd, Phr. M., Ph. D., 1898
www.ibiblio.org/herbmed/eclectic/kings/alpinia-offi.html
Plant identification characters
A perennial herb bearing stems about 1 m. in height which are covered
by the leaf sheaths of narrow lanceolate leaves. The inflorescence is a short
raceme of white flowers that are shaded and veined with dull red. -- UHM
The stem is from 2 to 4 feet high, erect, and bears a close resemblance to the
common cultivated canna, or shot plant. The parallel-veined leaf blades are
about a foot long, 2 to 4 inches wide, smooth, entire, and sharply acuminate.
They are attached at the base to a scarious, margined sheath, which clasps the
stem. The flowers are borne in a terminal dense spike; they consist of a short,
tubular, superior calyx, a white corolla, with 3 lobes, a large ovate labellum
marked with red veins, a single anther-bearing stamen, and a pistil with an
inferior ovary and a slender style (Bentley and Trimen, Med. Plants). --
King's American Dispensatory. Harvey Wickes Felter, M.D.,
and John Uri Lloyd, Phr. M., Ph. D., 1898
www.ibiblio.org/herbmed/eclectic/kings/alpinia-offi.html
Distribution in Myanmar:
Insein, Hanthawaddy, Hsi-seng, Yawnghwe,
Heho, Kalaw, Hsu-ga (Southern Shan State) -- UHM
Part used and uses:
Rhizome used as aromatic stimulant, condiment, carminative. -- UHM
Galangal is a stimulating aromatic, and has been successfully employed to aid
the digestive process, preventing fermentation and removing flatus. It will be
found especially useful in some forms of dyspepsia, preventing vomiting or
sickness of the stomach, and facilitating digestion. It may be used in all cases
in which a stimulating aromatic is indicated. It has some reputation as a remedy
for perineal relaxation with hemorrhoids, and for a lax and
pendulous abdomen. Its best form of administration is in tincture, the
dose of which is from 1/2 to 1 fluid drachm. The powder
may be given in doses of 15 to 20 grains; from 30 to 60 grains may be given in
infusion. It is rarely prescribed at the present day.--
King's American Dispensatory. Harvey Wickes Felter, M.D.,
and John Uri Lloyd, Phr. M., Ph. D., 1898
www.ibiblio.org/herbmed/eclectic/kings/alpinia-offi.html
Constituents:
1. 0.5 to 1.0 % of a cineol containing volatile oil
2. Soft acrid resin containing a pungent principle, galangol
3. Three yellowish crystalline principles: Alpinin, Galangin
and Kaemferid. (1) -- UHM
The constituents of galangal are similar to those of ginger. A volatile oil is
obtained by distilling the root with water, which possesses a camphoraceous
smell resembling that of cajeput oil. This is due, according to Schimmel & Co.
(1890), to the presence of appreciable amounts of cineol. It is soluble
in alcohol, and is lighter than water. A soft resin, having a pungent taste, is
extracted by ether, and also a peculiar, crystalline substance, named by Brandes
(1839), kaempferid. Jahns (1881) differentiated the kaempferid of Brandes
into three compounds, all forming yellow crystals, viz., kaempferid
(C16H12O6, fusing at 222° C. (431.6° F.), almost insoluble in water, and soluble with
difficulty in alcohol; galangin (C15H10O5, fusing at 214° C. (417.2° F.),
soluble in 34 parts of absolute and 68 parts of 90 per cent alcohol; and alpinin
(C17H12O6), fusing at 173° C. (343.4° F.). Kaempferid, by oxidation with
nitric acid, forms anisic acid (C6H4[OCH3]COOH), oxalic acid and other products.
Galangin similarly yields benzoic and oxalic acids (Amer. Jour. Pharm.
, 1882, p. 288). Kostanecki and Harry M. Gordin (Dissert., 1897),
showed kaempferid to be a flavonol derivative and established
its exact graphic formula. Probably galangin is similarly
constituted. Thresh (Pharm. Jour. Trans., Vol. XV., 1884, p. 234),
announced the presence of a pungent principle, which he designated galangol, and
gave the tabulated results of a complete analysis of the root, which shows as
much as 23.7 per cent of starch. --
King's American Dispensatory.
Harvey Wickes Felter, M.D., and John Uri Lloyd, Phr. M., Ph. D., 1898
www.ibiblio.org/herbmed/eclectic/kings/alpinia-offi.html
Contents of this page
syn C. domestica
Family: Zingiberaceae
UKT: Popularly known and sometimes spelled as
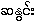 {hsa.nwing:}
{hsa.nwing:}
Burmese-Myanmar transcript names:
Agri.Dept.2000 32-0840:
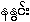 {na.nwing:}
{na.nwing:}
Chklist:
LSR 227:
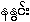 {na.nwing:}
{na.nwing:}
FAO : NL
KS-TMN: NL
Nagathein 2-101:
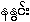 {na.nwing:} or
{na.nwing:} or
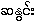 {hsa.nwing:}
{hsa.nwing:}
UHM 19: Hsa-nwin
Myanmar-Script Spelling
Official Myanmar Dictionaries :
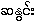 {hsa.nwing:} -- see
{hsa.nwing:} -- see
 {na.nwing:} --TravPo-M-Dict
099
{na.nwing:} --TravPo-M-Dict
099
 {na.nwing:}
-
{na.nwing:}
-
 --TravPo-M-Dict
159
--TravPo-M-Dict
159
 {na.nwing:}
- n. tumeric. Curcuma longa - Myan-Engl-Dict 220
{na.nwing:}
- n. tumeric. Curcuma longa - Myan-Engl-Dict 220
Chklist data:
Hindi:

Sanskrit:
English common name used in Myanmar :
Agri.Dept.2000 32-0840: Turmeric
FAO : NL
Lθ-seik-shin 227: turmeric
KS-TMN: NL
Nagathein 2-101: NG
UHM 19: Tumeric rhizome, Yellow Root, Saffron
Curcuma, turmeric -- Tropical Plant Database
www.rain-tree.com/tumeric.htm
Picture :
Leader -
www.rain-tree.com/plantimages.htm
Photo:
www.rain-tree.com/plantimages.htm
Plant identification characters :
A perennial herb whose underground portion consists of an erect, ovate or
pyriform fleshy rhizome which gives rise to less fleshy elongated branches
(secondary rhizomes) roots and leaves. -- UHM
Distribution in Myanmar:
Dry Zone, Chin Hills -- UHM
Part
used and uses :
Prepared rhizome. Used as Stimulant, condiment -- UHM
Root, Rhizome. Anti-inflammatory, Antioxidant,
Anti-mutagenic, Anti-cancerous, Cholagogueue, Depurative, Diuretic, Fumitory,
Hemostatic, Hepatoprotective, Lactagogue, Stomachic, Tonic, Vulnerary. See
Medline Abstracts on Internet from National Library of Medicine, 8600
Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20894 -- Tropical Plant Database
www.rain-tree.com/tumeric.htm
Ethnobotany (Worldwide use):
Brazil -- Bite (Leech), Bruise, Catarrh, Cholagogueue, Colic,
Congestion, Dysentery, Gonorrhea, Smallpox, Wound. China --
Amenorrhea, Antibilious, Balsamic, Cholagogueue, Colic, Congestion,
Hemostat, Stomachic. Java -- Abscess, Cold, Conjunctivitis,
Cosmetic, Gravel, Jaundice, Lactagogue, Parturition, Pyuria, Scabies, Wound.
Malaya -- Amenorrhea, Diarrhea, Diuretic, Dysentery,
Gonorrhea, Hepatosis, Sore, Swelling, Tonic, Urogenital. Nepal --
Depurative, Dermatosis. Elsewhere -- Bite (Leech), Bruise, Catarrh, Chickenpox,
Cold, Escharotic, Fumitory, Smallpox, Wound -- Tropical Plant Database
www.rain-tree.com/tumeric.htm
Constituents:
1. About 5 % volatile oil. 2. 0.3 % Curcumin, a yellow crystalline substance
which dissolves in alcohol forming a deep yellow solution.
3. Starch - 30 to 40 %. 4. Resin (7) -- UHM
1. Yellow colouring matter (curcumin);
2. p,p-dihydroxydicinnaoylmethane;
3. p-hydroxycinnamoylferuloylmethane;
4. p,α-dimethylbenzyl alcohol;
5. 1-methyl-4-acetyl-1-cyclohexene;
6. turmerone;
7. α-phellandrene;
8. sabinene;
9. zingiberene;
10. cineol;
11. borneol;
12. caprylic acid -- Merck Index,
p.1749
Plant chemicals include: 1,8-cineole, 2-bornanol, 2-hydroxy-methyl-anthraquinone,
4-hydroxy-cinnamoyl-(Feruloyl)-methane, Alpha-atlantone, Alpha-pinene, Alpha-terpineol,
Ar-turmerone, Arabinose, Ascorbic-acid, Ash, Azulene, Beta-carotene, Beta-pinene,
Beta-sesquiphellandrene, Bis-(Para-hydroxy-cinnamoyl)-methane, Bis-desmethoxycurcumin,
Bisabolene, Borneol, Boron, Caffeic-acid, Calcium, Caprylic-acid, Caryophyllene,
Chromium, Cineole, Cinnamic-acid, Cobalt, Copper, Cuminyl-alcohol, Curcumene, Curcumenol,
Curcumin, Curdione, Curlone, Curzerenone, Curzerenone-c, Cyclo-isoprenemyrcene,
D-alpha-phellandrene, D-camphene, D-camphor, D-sabinene, Dehydroturmerone,
Desmethoxycurcumin, Di-p-coumaroyl-methane, Dicinnamoylmethane, Didesmethoxycurcumin,
Diferuloyl-methane, Dihydrocurcumin, EO, Eugenol, Feruloyl-p-coumaroyl-methane,
Gamma-atlantone, Guaiacol, Isoborneol, L-alpha-curcumene, L-beta-curcumene, Limonene,
Manganese, Monodesmethoxycurcumin, Niacin, Nickel, O-coumaric-acid, P-coumaric-acid,
P-cymene, P-methoxycinnamic-acid, P-tolymethylcarbinol, Phosphorus, Protocatechuic-acid,
Resin, Riboflavin, Syringic-acid, Terpinene, Terpineol, Thiamin, Turmerone, Ukonan-a,
Ukonan-b, Ukonan-c, Ukonan-d, Vanillic-acid, Zingiberene -- Tropical Plant Database
www.rain-tree.com/tumeric.htm
Contents of this page
Family: Zingiberaceae (ginger family)
Burmese-Myanmar transcript names:
Agri.Dept.2000 40-1056:
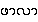 {hpa-la}/
{hpa-la}/
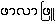 {hpa-la-hpru}
{hpa-la-hpru}
Chklist:
LSR 309:
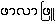 {hpa-la-hpru}
{hpa-la-hpru}
FAO : NL
KS-TMN: NL
Nagathein 2-304:
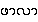 {hpa-la}
{hpa-la}
UHM 23: Hpala
Myanmar-Script Spelling
Official Myanmar Dictionaries:
 {hpa-la}
-
{hpa-la}
-
 -- TravPo-M-Dict
207
-- TravPo-M-Dict
207
 {hpa-la}
- n. cardamom plant, Elettaria cardamomum -- Myan-Engl-Dict 297
{hpa-la}
- n. cardamom plant, Elettaria cardamomum -- Myan-Engl-Dict 297
Chklist data:
Hindi:

Sanskrit:
English common name used in Myanmar :
Agri.Dept.2000 40-1056: Lesser cardamon
Chklist:
LSR 309:
 {hpa-la-hpru}
{hpa-la-hpru}
FAO : NL
KS-TMN: NL
Nagathein 2-304:
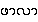 {hpa-la}
{hpa-la}
UHM 23: Cardomom seed
Picture :
Leaders: left - colour drawing -
www.indianspices.com/html/spfarm_sc.htm; right - photo clump -
www.floridata.com/ref/E/elet_car.cfm
Photo: left - leaves -
www.ibiblio.org/herbmed/pictures/p05/pages/elettaria-cardamomum.htm ; right
- flower and fruit --
www.pioneerherbs.com/ellataria_cardamomum.htm
Plant identification characters :
A perennial herb attaining a height of 6-12" leaves lanceolate and
borne on long sheathing stems, flowers borne on horizontal racemes that arise
from the rhizome horizontally along the ground, fruit an ovoid, loculicidally
dehiscent capsule, seeds covered by an aril. -- UHM
Cardamom is a rather typical looking ginger plant except that it is huge,
standing as much as 12 ft ( 3.7 m) tall. Thick, fleshy rhizomes give rise to
erect shoots that bear two rows of linear-lance-shaped leaves each about 2 ft
(0.6 m) long. The leaves are smooth and dark green above, silky and paler
beneath. They taper to an acute point. The inflorescences develop on separate,
horizontal stems that spread along the ground. They are loose panicles about 2
ft (0.6 m) long, consisting of many small blossoms that have white or yellowish
petals with lilac veins and pink or yellow margins. The fruits are thin-walled,
smooth-skinned, oblong, greenish capsules about 3/4 in (1.9 cm) long. Each
contains 15-20 aromatic reddish brown seeds. Cardamom grows
wild in the Ghat Mountains on the Malabar Coast of SW India, in an area known as
the Cardamom Hills. It occurs in the understory of tropical rain forests at
elevations of 2500 - 5000 ft (762-1524 m), where it rains about 150 in (381 cm)
per year. It also grows in similar habitats in Sri Lanka. Cardamom is cultivated
commercially in India, Sri Lanka, Guatemala and Tanzania.
Moisture: Cardamom grows with its roots continually wet. It needs constant
moisture. It does okay if the rain stops for a short period, once in a while!
Hardiness: USDA Zones 10 - 12. A constant temperature around 72ΊF (22ΊC)
is best. Cardamom suffers at temperatures below 50ΊF (10ΊC).
Cardamom usually is propagated by division of rhizomes. --
www.floridata.com/ref/E/elet_car.cfm
Distribution in Myanmar:
Tenasserim, Mergui, Tavoy, Thaton, Ataran,
Kado, Kawkareik, Pa-an, Mobyai, Pelong (Southern Shan State) -- UHM
Part used
and uses:
Dried ripe seed recently removed from the capsules. Used as carminative,
aromatic and condiment. -- UHM
Ancient Indians, more than 1000 years before Christ, used cardamom medicinally
to treat various maladies. Cardamom, like cinnamon and ginger, is a stimulant,
and is said to relieve indigestion, flatulence and headaches. The Greeks and
Romans used it as a culinary spice. False cardamom, from other
kinds of gingers in the genera Amomum and Aframomum, is produced
in Thailand and Cambodia, and sold as a substitute for (or counterfeit of) the
real thing. --
www.floridata.com/ref/E/elet_car.cfm
Constituents:
1. 3-7 percent of volatile cardamom oil containing terpineol, terpinyl
acetate, cineol, borneol and probably sabinene.
2. Fixed oil.
3. Protein, Calcium oxalate and silica (7) -- UHM
Contents of this page
MMPDB:
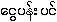 {ngwι-pan:ping}
{ngwι-pan:ping}
Family : Zingiberaceae
Ref. Burmese-Myanmar
transcripts
Agri.Dept.2000 15-0390:
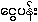 {ngwι-pan:}
{ngwι-pan:}
FAO :
NL
Lθ-seik-shin :
NL
KS-TMN:
NL
Nagathein 1-209:
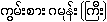 {kwam:sa:ga.moan: (kri:)}
{kwam:sa:ga.moan: (kri:)}
UHM : NL
UKT: Nagathein 1-209 refutes the identification of Hedychium spicatum
as {ngwι-pan:} citing "{wa.nau-tha.Di. san~dau-da.ya.} volume 2
introduction to {kap~pu-ra.ka-kya-ri}. [UKT: {kap~pu-ra.} refers to "camphor".]
Myanmar-Script Spelling
Official Myanmar Dictionaries :
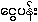 {ngwι-pan:} -
{ngwι-pan:} -
 - TravPo-M-Dict
075
- TravPo-M-Dict
075
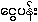 {ngwι-pan:} - n. plant of the ginger family white waxy flowers.
Hedychium spicatum - Myan-Engl-Dict 098
{ngwι-pan:} - n. plant of the ginger family white waxy flowers.
Hedychium spicatum - Myan-Engl-Dict 098
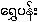 {rhwι-pan:} - n. 1. yellow ginger lily. Hedychium coronarium
. 2. male genitals - Myan-Engl-Dict 422
{rhwι-pan:} - n. 1. yellow ginger lily. Hedychium coronarium
. 2. male genitals - Myan-Engl-Dict 422
Chklist data:
Hindi :
Sanskrit :
English common name used in Myanmar :
Agri.Dept.2000 15-0390: Garland flower
Chklist:
LSR :
NL
FAO :
N
KS-TMN:
NL
Nagathein 1-209:
NG
UHM : NL
UKT: See USDA-NRCS for "Garland flower". Only "White
Garland lily" is listed. Are the two the same? Notice there are two species
given by USDA-NRCS :
Hedychium coronarium Koenig -- white garland-lily fam.
Zingiberaceae
Hedychium flavescens Carey ex Roscoe -- cream garland-lily fam.
Zingiberaceae
Are "white garland-lily"
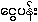 {ngwι-pan:} (literally - "silver flower") and "cream garland-lily"
{ngwι-pan:} (literally - "silver flower") and "cream garland-lily"
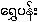 {shwι-pan:} (literally "gold flower") ?
{shwι-pan:} (literally "gold flower") ?
Picture :
Plant identification characters :
Distribution in Myanmar :
Part
used and uses :
Constituents :
Contents of this page
Family : Zingiberaceae
Ref. Burmese-Myanmar
transcripts
Agri.Dept.2000 10-0242:
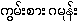 {kwam:sa:ga.moan:}
{kwam:sa:ga.moan:}
Chklist:
Lθ-seik-shin :
NL
FAO :
NL
KS-TMN:
NL
Nagathein 1-210:
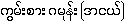 {kwam:sa:ga.moan: (a.ngθύ)}
{kwam:sa:ga.moan: (a.ngθύ)}
UHM : NL
Myanmar-Script Spelling
Official Myanmar Dictionaries :
 {kwam:sa:ga.moan:} is not listed.
{kwam:sa:ga.moan:} is not listed.
 {ga.moan:} -
{ga.moan:} -
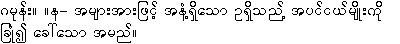 - TravPo-M-Dict
064
- TravPo-M-Dict
064
 {ga.moan:} - n. generic term for some herbs with aromatic tubers (these
are most likely kaempferia from ginger family but also include a few from
the orchid and lily families. - Myan-Engl-Dict 084
{ga.moan:} - n. generic term for some herbs with aromatic tubers (these
are most likely kaempferia from ginger family but also include a few from
the orchid and lily families. - Myan-Engl-Dict 084
Chklist data:
Hindi : {kyan-dra.mul} -- Nagathein
(UKT: Nagathein is giving the transcription in Burmese-Myanmar.
However, the onset of the first syllable is च {sa.}
and the name in Pali-Myanmar is most likely {san~da.mu-la.}. If so, it is most
likely related to {san~da.ku:} from which the word 'camphor' is derived. --
point to be checked with my peers.)
Sanskrit :
English common name used in Myanmar :
Agri.Dept.2000 10-0242: NG
Chklist:
LSR : NL
FAO :NL
KS-TMN: NL
Nagathein 1-210:NG
UHM : NL
Picture :
Plant identification characters :
 There are two kinds: the large and the small. The small one grows close to the
ground -- a short plant. It has no above-ground stem. What is known in Myanmar
country as {kwam:sa: ga.moan°:} is the small one. [UKT: sic. Kaempferia galanga] The large kind has an upright stem, and is known as
There are two kinds: the large and the small. The small one grows close to the
ground -- a short plant. It has no above-ground stem. What is known in Myanmar
country as {kwam:sa: ga.moan°:} is the small one. [UKT: sic. Kaempferia galanga] The large kind has an upright stem, and is known as
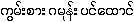 {kwam:sa: ga.moan°: ping-htaung}. [UKT: Hedychium spicatum - Nagathein
1-209]. It is similar to
{kwam:sa: ga.moan°: ping-htaung}. [UKT: Hedychium spicatum - Nagathein
1-209]. It is similar to
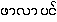 {hpa-la ping} [UKT: Amomum subulatum ?] and
{hpa-la ping} [UKT: Amomum subulatum ?] and
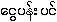 {ngwι-pan: ping} --
which leads some [UKT: such as Agri.Dept.2000 15-0390?] to call it erroneously as
{ngwι-pan: ping} --
which leads some [UKT: such as Agri.Dept.2000 15-0390?] to call it erroneously as
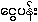 {ngwι-pan:}. Both the large and the small {kwam:sa: ga.moan°:} is used in
medicine. In India, the large is grown extensively because it is of greater use.
In Myanmar, since the larger one is imported from India, it is sometimes called
the "Indian-{kwam:sa: ga.moan°:}" and is used in "blood" and anti-pyretic
tonics. -- Nagathein, free translation by UKT.
{ngwι-pan:}. Both the large and the small {kwam:sa: ga.moan°:} is used in
medicine. In India, the large is grown extensively because it is of greater use.
In Myanmar, since the larger one is imported from India, it is sometimes called
the "Indian-{kwam:sa: ga.moan°:}" and is used in "blood" and anti-pyretic
tonics. -- Nagathein, free translation by UKT.
Note: According to Nagathein 1-209, Hedychium spicatum - is the
large-{kwam:sa: ga.moan°:}, and not
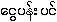 {ngwι-pan: ping}. He does not mention what
{ngwι-pan: ping}. He does not mention what
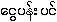 {ngwι-pan: ping} is. (to be checked again.).
{ngwι-pan: ping} is. (to be checked again.).
Distribution in Myanmar :
Part
used and uses :
Constituents :
Contents of this page
Family : Zingiberaceae
Ref. Burmese-Myanmar
transcripts
Agri.Dept.2000 45-1189:
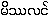 {maith~tha.ling}
{maith~tha.ling}
-- Zingiber barbatum (not listed in USDA-NRCS)
Chklist:
LSR 359 :
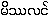 {maith~tha.ling}
{maith~tha.ling}
-- Zingiber consumunar (wrong spelling?)
FAO :
NL
KS-TMN 225:
Meik-thalin -- Zingiber cassumunar
Nagathein 2-453:
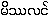 {maith~tha.ling}
{maith~tha.ling}
-- Zingiber consumunar (wrong spelling?)
UHM : NL
Romabama note: See compound
vowels for transliteration:
{maith~tha.ling}
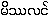
{meith~tha.ling}
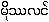 (non-existent word)
(non-existent word)
UKT: Because of the uncertainty in the spellings given by Agri.Dept.2000,
LSR, and Nagathein, I checked with USDA-NRCS (Chklist online was
not accessible in 2006 June because of Myanmar ISPs' failure) and found:
- Zingiber barbatum (not listed in USDA-NRCS)
- Zingiber consumunar (wrong spelling): correct spelling is Zingiber cassumunar
Myanmar-Script Spelling
Official Myanmar Dictionaries :
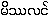 {maith~tha.ling} -
{maith~tha.ling} -
 - TravPo-M-Dict
245
- TravPo-M-Dict
245
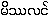 {maith~tha.ling} - n. ginger-like herb, the rhizome of which smells
like camphor, has a hot taste, and is used medicinally. Zingiber barbatum. - Myan-Engl-Dict
359
{maith~tha.ling} - n. ginger-like herb, the rhizome of which smells
like camphor, has a hot taste, and is used medicinally. Zingiber barbatum. - Myan-Engl-Dict
359
Hindi :

{gyin-ga.li. a.drak} -- Nagathein
Sanskrit :
English common name used in Myanmar:
Agri.Dept.2000 45-1189: wild ginger
Chklist:
LSR 359 : wild ginger
FAO :
NL
KS-TMN 225:
NG
Nagathein 2-453: NG
UHM : NL
Picture :
Leader - Nagathein
Photo: Photos:
left -- habit with pedunculate spikes;
right -- cultivated plants.
Click on the pictures to enlarge. -- KS-TMN
Plant identification characters :
A perennial herb; rhizomes horizontal creeping, tuberous, cylindrical to ovoid,
irregular, palmately and profusely branched, laterally compressed, strongly
aromatic; aerial stems leafy, cylindrical, erect, annual. Leaves alternate, distichous, simple, subsessile or shortly petiolate; leaf sheaths oblong, with
membranous margins; ligules ovate, membranous. Inflorescences radical, spikes
cylindrical, fusiform or cone-like, borne on a peduncle produced from rootstock;
bracts outer and inner, spirally arranged, very dense, persistent, reddish
white, the outer broadly ovate to sub-orbicular, cucullate, the inner ovate,
glabrous. Flowers ebracteolate, bisexual, zygomorphic, trimerous, epigynous.
Calyx synsepalous, cylindrical, 3-toothed, the tubes split half way down,
whitish, deciduous. Corolla synpetalous, unequally 3-lobed, the posterior lobe
elliptic-lanceolate, erect and concave, the laterals lanceolate, deflexed,
yellowish white, deciduous. Androecium of 1 fertile stamen, epipetalous at the
mouth of corolla tube, inserted, the filaments very short, deeply grooved,
yellowish white, with purplish mottlings at the dorsals of bases, the anthers
dithecous, oblongoid, appendix or beak curved, introrse, dehiscence
longitudinal; lip or labellum 3-lobed, as long as the corolla lobes, attached at
the mouth of corolla tube, opposite the fertile stamen, the middle lobe
orbicular, emarginate, the 2 laterals or the basal auricles large, ovate or
oblong-obtuse, crisped, yellowish white with reddish purple mottlings. Pistil 1,
ovary triangular or 3-lobed, tomentose, 3-carpelled, syncarpous, 3-loculed, the
placentation axile, the ovules many, superposed, the style filiform, passing
through the channel of two anther lobes and appendix of connectives, the
filiform processes 2, acicular, at anterior side of style bases, the stigma
cupuliform, ciliate. Fruit a dehiscing capsule, globose or globosely oblongoid;
seeds large, globosely oblongoid, arillate. Flowering period: April-July.
Fruiting period: June-August. -- KS-TMN
Distribution in Myanmar :
Grows wild especially in lower Myanmar. Commonly cultivated. -- KS-TMN
Part
used and uses :
Rhizome -- Amenorrhoea; Gastrointestinal colic; Dysentery;
Haemorrhoid; Skin disease; Antidote for snake venom; Indigestion. -- KS-TMN
Constituents :
Contents of this page
Family: Zingiberaceae
Burmese-Myanmar transcript names:
Agri.Dept.2000 13-0317:
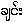 (
(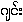 ) {hkying:
(gying:)}/
) {hkying:
(gying:)}/
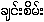 (
(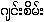 ) {hkying:seim: (gying: seim:)}
) {hkying:seim: (gying: seim:)}
Chklist:
LSR 117:
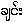 (
(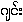 ) {hkying:
(gying:)}
) {hkying:
(gying:)}
FAO : NL
KS-TMN: NL
Nagathein 1-290:
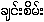 {hkying:seim:}
{hkying:seim:}
UHM 44: Gyin
Romabama note by UKT: The official spelling of the name of the plant is
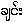 . It is a monosyllabic word, and the onset of the syllable in IPA (International
Phonetic Alphabet) is /ʧ/ pronounced similar to English [ch] in <church>
/ʧɜːʧ/. In Burmese-Myanmar
/ʧ/ is spelled with r1c2 {hka.} which is conjoined
with r6c1 {ya.} resulting in the conjunct {hkya.}. The syllable
. It is a monosyllabic word, and the onset of the syllable in IPA (International
Phonetic Alphabet) is /ʧ/ pronounced similar to English [ch] in <church>
/ʧɜːʧ/. In Burmese-Myanmar
/ʧ/ is spelled with r1c2 {hka.} which is conjoined
with r6c1 {ya.} resulting in the conjunct {hkya.}. The syllable
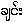 is thus generically spelled in Romabama (a one-to-one transliteration) as {hkying:}.
However, it is commonly transcribed as "chin". Please note that I am engaged in
MMPDB because of my interest in the Myanmar akshara (which is based on phonetic
principles), and I am following the Romabama rules of transliteration. The
Burmese-Myanmar names are thus given according to the Burmese-Myanmar spellings.
is thus generically spelled in Romabama (a one-to-one transliteration) as {hkying:}.
However, it is commonly transcribed as "chin". Please note that I am engaged in
MMPDB because of my interest in the Myanmar akshara (which is based on phonetic
principles), and I am following the Romabama rules of transliteration. The
Burmese-Myanmar names are thus given according to the Burmese-Myanmar spellings.
Myanmar-Script Spelling :
Official Myanmar Dictionaries:
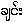 {hkying:} -
{hkying:} -
 --
TravPo-M-Dict 053
--
TravPo-M-Dict 053
 {hkying:}- n. ginger - Myan-Engl-Dict 071
{hkying:}- n. ginger - Myan-Engl-Dict 071
 {hkying:seim:} - n. ginger - Myan-Engl-Dict 071
{hkying:seim:} - n. ginger - Myan-Engl-Dict 071
 {hkying:thoap} - n. ginger salad- Myan-Engl-Dict 071
{hkying:thoap} - n. ginger salad- Myan-Engl-Dict 071
UKT: No matter what the Burmese-Myanmar spelling is the pronunciation according
to the
Official Myanmar Dictionary is {gying:}.
Hindi
:

Hindi adrak [अदरख]
(fresh and green), sonth
[सोंठ]
(dried), Pali singivera
[सिंगिवेर];
the corresponding Sanskrit form is shringavera
[शृंगवेर].
These Indic names used to be explained to mean shaped like a deer's antler (horn)
--
www.uni-graz.at/~katzer/engl/generic_frame.html?Zing_off.html
Sanskrit :
shringavera
[शृंगवेर]
English common name used in Myanmar :
Agri.Dept.2000 13-0317: Ginger
Chklist:
LSR 117: Ginger
FAO : NL
KS-TMN: NL
Nagathein 1-290: Ginger

UHM 44: Ginger Rhizome
Picture
Leader -
www.uni-graz.at/~katzer/engl/generic_frame.html?Zing_off.html
Photo: left - inflorescence; right - tuber; right-lower - stem and tubers
--
www.uni-graz.at/~katzer/engl/generic_frame.html?Zing_off.html
Plant
identification characters :
A perennial herb with a subterranean, digitately branched rhizome that sends
up stems that are covered by leaf sheaths, leaves alternate, smooth, pale green
and lanceolate, flowers orange-yellow forming an ovate-oblong spike. -- UHM
Distribution in Myanmar:
Nyaung-don, Danu-phyu. etc. -- UHM
Part used and uses:
The dried rhizome with outer cortical layers either partially or completely
removed. -- UHM
The large, fleshy rhizome (gingerroot, although it is not a root). In the
fresh state, it has a characteristic staghorn-like appearance; dried ginger is
usually sold in form of a off-white to very light brown powder. Ginger leaves
are occasionally used for flavouring in ginger producing countries. --
www.uni-graz.at/~katzer/engl/generic_frame.html?Zing_off.html
Constituents :
1. 1-3 percent of volatile oil, consisting for the most part terpenes,
phellandrine and dextro-camphene and the sesquiterpine zingiberene.
2. Zingerone - extremely pungent crystaline substance chemically related to
capsaicin, which gives its hot pungent taste.
3. Resins and starch. (7) -- UHM
The essential oil (1 to 3% of the fresh rhizome) contains mostly
sesquiterpenes, e.g., (-)-zingiberene (up to 70%), (+)-ar-curcumene, β-sesquiphellandrene,
bisabolene and farnesene. Monoterpenoids occur in traces (β-phelladrene, cineol, citral).
The pungency of ginger is caused by a non-volatile resin containing
the same type of hydroxyaryl compounds that are also found in other spices of the
ginger family: Zingerone, gingeroles and shoagoles. The pungent gingeroles
degrade to the milder shoagoles during storage; high gingerole content and good
pungency thus indicate freshness and quality. See also
grains of paradise. --
www.uni-graz.at/~katzer/engl/generic_frame.html?Zing_off.html
Chemics experience:
Hydro-distillation of freshly diced fresh rhizome yielded an essential oil or
refractive index 1.475 - 1.477 (30°C.).; yield: 1 ml/kg of fresh rhizomes.
The distillation residue or spent-residual ginger was considered to be almost
deplete of its essential oil and when air-dried was referred to "dried ginger".
Yield of dried ginger: -- kg per kg of fresh rhizomes. Dried ginger when extracted with ethanol
yielded a reddish
brown tincture. Partial evaporation of ethanol yielded a thick yellowish syrup.
Yield: Based on 1 kg of fresh rhizomes:
Essential oil: 1.5 ml (av. of 9 runs)
Dried ginger: 0.41 kg. (av. of 5 runs)
Contents of this page
Agri.Dept.2000 lists 3 species of {pa.tθ:kau:}
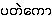
34-0895: A. officinarum - {pa.tθ:kau:ka.lι:}
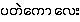 -
literal meaning: "small" {pa.tθ:kau:}
-
literal meaning: "small" {pa.tθ:kau:}
- Lesser galangal
34-0896: A. galanga - {pa.tθ:kau:kri:}
 -
literal meaning: "large" {pa.tθ:kau:}
-
literal meaning: "large" {pa.tθ:kau:}
- Greater galangal
34-0897: A. nutans - {pa.tθ:kau:lat}
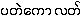 - literal meaning: "medium" {pa.tθ:kau:}
- literal meaning: "medium" {pa.tθ:kau:}
- Nutral galangal
Chklist online is not available to Myanmar internet ISP servers' failure in
2006 June
USDA-NRCS
"ALPIN","Alpinia Roxb.","alpinia","Zingiberaceae"
"ALGA2","Alpinia galanga (L.) Sw.","greater galangal","
Zingiberaceae"
"LAGA5","Languas galanga (L.) Stuntz","&
gt;>Alpinia galanga","Zingiberaceae"
"ALMU2","
Alpinia mutica Roxb.","small shell ginger","Zingiberaceae"
"ALOF4","Alpinia officinarum Hance","lesser galangal","
Zingiberaceae"
"LAOF","Languas officinarum (Hance) Farw.","
>>Alpinia officinarum","Zingiberaceae"
"ALPU4","Alpinia purpurata (Vieill.) K. Schum.","
red ginger","Zingiberaceae"
"ALZE","Alpinia zerumbet
(Pers.) Burtt & R.M. Sm.","shellplant","Zingiberaceae"
"ALNU3","Alpinia nutans (L.) Roscoe",">>Alpinia zerumbet",
"Zingiberaceae"
"ALSP","Alpinia speciosa (Wendl.) K. Schum.","
>>Alpinia zerumbet","Zingiberaceae"
"CASP15","Catimbium speciosum (Wendl.) Holttum",
">>Alpinia zerumbet","Zingiberaceae"
"LASP7","Languas speciosa (Wendl.) Merr.",">>Alpinia
zerumbet","Zingiberaceae"
Contents of this page
Family : Zingiberaceae
Chklist online is not available to Myanmar internet ISP servers' failure in
2006 June
USDA-NRCS
"HEDYC","Hedychium Koenig","garland-lily","Zingiberaceae"
"HECO11","Hedychium coronarium Koenig","white
garland-lily","Zingiberaceae"
"HEFL5","Hedychium flavescens Carey ex Roscoe","cream garland-lily","Zingiberaceae"
"HEFL12","Hedychium flavum auct. non Roxb. [misapplied]",">>Hedychium
flavescens","Zingiberaceae"
"HEGA","Hedychium gardnerianum Shepard ex Ker-Gawl.","Kahila garland-lily","Zingiberaceae"
Contents of this page
Family : Zingiberaceae
Chklist online is not available to Myanmar internet ISP servers' failure in
2006 June
USDA-NRCS
"KAPA3","Kaempferia pandurata Roxb.",">>Boesenbergia
rotunda","Zingiberaceae"
"KAEMP2","Kaempferia L.","kaempferia","Zingiberaceae"
"KAGA2","Kaempferia galanga L.","galanga","Zingiberaceae"
"KARO2","Kaempferia rotunda L.","kaempferia","Zingiberaceae"
"KARO3","Kaempferia rotundata L. [orthographic error]",">>Kaempferia
rotunda","Zingiberaceae"
Contents of this page
UKT: The family Zingiberaceae is of interest to me because most of the
members are aromatic. During my chemical research days in Myanmar, because of
the lack of suitable detectors I had to rely mostly on my own nose to identify
the essential oils, and this family had been important to me. You will find
below the very extensive list of the species of the family many of which can be
expected to be found in the Shan State (I was posted at Taunggyi College -- now
Taunggyi University) the capital of which is Taunggyi.
Results of search for 'Amomum' in the Checklist of Plants of
Myanmar, U.S. National Herbarium, 15 Jul 2006.
Aframomum angustifolium K. Schum. Cited as: Amomum angustifolium
Sonn. Habit: Herb. Distribution: Cultivated. Common Names: Bengal cardamon
Amomum aculeatum Roxb. Habit: Herb. Distribution: Taninthayi
Amomum aromaticum Roxb. Habit: Herb. Distribution: Cultivated. Common Names: Bengal cardamon
Amomum corynostachyum Wall. Habit: Herb. Distribution: Bago, Kayin, Mon. Common Names: Gonmin
Amomum dealbatum Roxb. Habit: Herb. Distribution: Sagaing
Amomum gramineum Wall. Habit: Herb. Distribution: Taninthayi
Amomum koenigii Baker. Habit: Herb. Distribution: Mandalay, Taninthayi. Common Names: Tough ginger
Amomum robertsonii Craib. Habit: Herb. Distribution: Shan
Amomum sericeum Roxb. Habit: Herb. Distribution: Sagaing. Common Names: Hpala
Amomum subulatum Roxb. Habit: Herb. Distribution: Cultivated. Common Names: Greater cardamon, Hpala-gyi
Amomum villosum Lour. Cited as: Amomum xanthioides Wall. Habit: Herb. Distribution: Taninthayi. Common Names: Xanthoid cardamon
Etlingera araneosa (Baker) R.M. Sm. Cited as: Amomum araneosum Baker,
Hornstedtia araneosa (Baker) K. Schum. Habit: Herb. Distribution: Taninthayi
Etlingera littoralis (Koenig) Giseke. Cited as: Amomum littorale Koenig,
Amomum megalocheilos Baker, Hornstedtia megalocheilos (Baker)
Ridley. Habit: Herb. Distribution: Taninthayi, Taninthayi
Etlingera sulphurea (R. Parker) R.M. Sm. Cited as: Amomum sulphurea R. Parker,
Hornstedtia sulfurea R. Parker. Habit: Herb. Distribution: Bago, Kachin, Mandalay, Taninthayi
USDA-NRCS
"AFRAM","Aframomum Schumann","aframomum","Zingiberaceae"
"AFME","Aframomum melegueta Schumann","melegueta pepper","Zingiberaceae"
"ALPIN","Alpinia Roxb.","alpinia","Zingiberaceae"
"ALGA2","Alpinia galanga (L.) Sw.","greater galangal","Zingiberaceae"
"LAGA5","Languas galanga (L.) Stuntz",">>Alpinia galanga","Zingiberaceae"
"ALMU2","Alpinia mutica Roxb.","small shell ginger","Zingiberaceae"
"ALOF4","Alpinia officinarum Hance","lesser galangal","Zingiberaceae"
"LAOF","Languas officinarum (Hance) Farw.",">>Alpinia
officinarum","Zingiberaceae"
"ALPU4","Alpinia purpurata (Vieill.) K. Schum.","red ginger","Zingiberaceae"
"ALZE","Alpinia zerumbet (Pers.) Burtt & R.M. Sm.","shellplant","Zingiberaceae"
"ALNU3","Alpinia nutans (L.) Roscoe",">>Alpinia zerumbet","Zingiberaceae"
"ALSP","Alpinia speciosa (Wendl.) K. Schum.",">>Alpinia
zerumbet","Zingiberaceae"
"CASP15","Catimbium speciosum (Wendl.) Holttum",">>Alpinia
zerumbet","Zingiberaceae"
"LASP7","Languas speciosa (Wendl.) Merr.",">>Alpinia
zerumbet","Zingiberaceae"
"AMOMU","Amomum Roxb.","cardamom","Zingiberaceae"
"AMCO12","Amomum compactum Sol. ex Maton","round cardamom","Zingiberaceae"
"AMKE2","Amomum kepulaga Sprague & Burkill",">>Amomum
compactum","Zingiberaceae"
"AMGR9","Amomum gracile Blume","serkkom","Zingiberaceae"
"BOESE","Boesenbergia Kuntze","boesenbergia","Zingiberaceae"
"BORO4","Boesenbergia rotunda (L.) Mansf.","rotund boesenbergia","Zingiberaceae"
"KAPA3","Kaempferia pandurata Roxb.",">>Boesenbergia
rotunda","Zingiberaceae"
"CURCU","Curcuma L.","curcuma","Zingiberaceae"
"CUAM4","Curcuma amada Roxb.","mango ginger","Zingiberaceae"
"CUAN2","Curcuma angustifolia Roxb.","east indian arrowroot","Zingiberaceae"
"CUAR3","Curcuma aromatica Salisb.","curcuma","Zingiberaceae"
"CUAU2","Curcuma australasica Hook. f.","","Zingiberaceae"
"CULO","Curcuma longa L.","common turmeric","Zingiberaceae"
"CUDO2","Curcuma domestica Val.",">>Curcuma longa","Zingiberaceae"
"CUZE","Curcuma zedoaria (Christm.) Roscoe","zedoary","Zingiberaceae"
"AMZE3","Amomum zedoaria Christm.",">>Curcuma zedoaria","Zingiberaceae"
"ELETT","Elettaria Maton","elettaria","Zingiberaceae"
"ELCA19","Elettaria cardamomum (L.) Maton","cardamom","Zingiberaceae"
"AMCA11","Amomum cardamomum L.",">>Elettaria cardamomum","Zingiberaceae"
"ETLIN","Etlingera Giseke","waxflower","Zingiberaceae"
"ETCE","Etlingera cevuga (Seem.) R.M. Sm.","waxflower","Zingiberaceae"
"ETEL","Etlingera elatior (Jack) R.M. Sm.","torch-ginger","Zingiberaceae"
"NIEL","Nicolaia elatior (Jack) Horan.",">>Etlingera
elatior","Zingiberaceae"
"PHMA27","Phaeomeria magnifica (Roscoe) K. Schum.",">>Etlingera
elatior","Zingiberaceae"
"HEDYC","Hedychium Koenig","garland-lily","Zingiberaceae"
"HECO11","Hedychium coronarium Koenig","white garland-lily","Zingiberaceae"
"HEFL5","Hedychium flavescens Carey ex Roscoe","cream garland-lily","Zingiberaceae"
"HEFL12","Hedychium flavum auct. non Roxb. [misapplied]",">>Hedychium
flavescens","Zingiberaceae"
"HEGA","Hedychium gardnerianum Shepard ex Ker-Gawl.","Kahila garland-lily","Zingiberaceae"
"HITCH","Hitchenia Wallich","hitchenia","Zingiberaceae"
"HICA11","Hitchenia caulina (J. Graham) Baker","chavar","Zingiberaceae"
"KAEMP2","Kaempferia L.","kaempferia","Zingiberaceae"
"KAGA2","Kaempferia galanga L.","galanga","Zingiberaceae"
"KARO2","Kaempferia rotunda L.","kaempferia","Zingiberaceae"
"KARO3","Kaempferia rotundata L. [orthographic error]",">>Kaempferia
rotunda","Zingiberaceae"
"RENEA","Renealmia L. f.","renealmia","Zingiberaceae"
"REAL2","Renealmia alpinia (Rottb.) Maas","jenjibre-de-jardin","Zingiberaceae"
"ALEX2","Alpinia exaltata (L. f.) Roemer & J.A. Schultes",">>Renealmia
alpinia","Zingiberaceae"
"AMAL6","Amomum alpinia Rottb.",">>Renealmia alpinia","Zingiberaceae"
"REEX","Renealmia exaltata L. f.",">>Renealmia alpinia","Zingiberaceae"
"REJA","Renealmia jamaicensis (Gaertn.) Horan.","narciso
colorado","Zingiberaceae"
"REJAP","Renealmia jamaicensis (Gaertn.) Horan. var. puberula (Gagnepain)
Maas","narciso colorado","Zingiberaceae"
"ALAN4","Alpinia antillarua auct. non Roemer & J.A. Schultes
[misapplied]",">>Renealmia jamaicensis var. puberula","Zingiberaceae"
"ALJA2","Alpinia jamaicensis Gaertn. p.p.",">>Renealmia jamaicensis var.
puberula","Zingiberaceae"
"REAN","Renealmia antillarua auct. non (Roemer & J.A. Schultes) Gagnepain
[misapplied]",">>Renealmia jamaicensis var. puberula","Zingiberaceae"
"REOC","Renealmia occidentalis (Sw.) Sweet","bijao","Zingiberaceae"
"ALAR3","Alpinia aromatica Aubl.",">>Renealmia
occidentalis","Zingiberaceae"
"ALOC4","Alpinia occidentalis Sw.",">>Renealmia
occidentalis","Zingiberaceae"
"REAR2","Renealmia aromatica (Aubl.) Griseb.",">>Renealmia
occidentalis","Zingiberaceae"
"ZINGI","Zingiber P. Mill.","ginger","Zingiberaceae"
"ZIMI4","Zingiber mioga (Thunb.) Roscoe","Mioga ginger","Zingiberaceae"
"ZIMO2","Zingiber montanum (Koenig) Theilade","Cassumunar ginger","Zingiberaceae"
"ZICA","Zingiber cassumunar Roxb.",">>Zingiber
montanum","Zingiberaceae"
"ZIPU2","Zingiber purpureum Roscoe",">>Zingiber montanum","Zingiberaceae"
"ZIOF","Zingiber officinale Roscoe","garden ginger","Zingiberaceae"
"AMZI","Amomum zingiber L.",">>Zingiber officinale","Zingiberaceae"
"ZIZI2","Zingiber zingiber (L.) Karst.",">>Zingiber
officinale","Zingiberaceae"
"ZIZE","Zingiber zerumbet (L.) Sm.","bitter ginger","Zingiberaceae"
"AMZE","Amomum zerumbet L.",">>Zingiber zerumbet","Zingiberaceae"
Contents of this page
Entry format: Botanical name / Family / Ref. Burmese-Myanmar
transcripts ( Agri.Dept.2000 :
Chklist: LSR : FAO : KS-TMN:
Nagathein :
UHM :/ Myanmar-Script Spelling (
Official Myanmar Dictionaries : - TravPo-M-Dict - Myan-Engl-Dict - Myan-Ortho
/ Chklist data / Hindi /
Sanskrit / English common name used in Myanmar / Picture /
Plant identification characters / Distribution in Myanmar / Part
used and uses / Constituents /
End of TIL file

 Hindi:
Hindi: